The Cyber Kill Chain
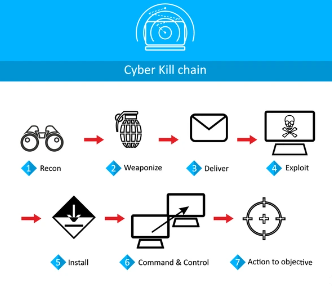
The cyber kill chain is a model developed by Lockheed Martin to describe the stages of a cyber-attack, from initial reconnaissance to exfiltration of sensitive data. Understanding the cyber kill chain is crucial for organizations to develop effective defense strategies and prevent cyber-attacks. In this article, we will explore the seven stages of the cyber kill chain and discuss prevention technologies that can be implemented at each step to thwart attackers.
Stage 1: Reconnaissance
In the reconnaissance stage, attackers gather information about the target organization, including its network infrastructure, systems, and vulnerabilities. This stage is often referred to as “information gathering” or “intelligence gathering.”
Prevention Technologies:
- Network Traffic Analysis (NTA): NTA solutions monitor network traffic to identify suspicious patterns and anomalies, allowing organizations to detect and respond to reconnaissance activities.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAFs): WAFs can detect and block suspicious traffic to web applications, preventing attackers from gathering information about the organization’s web presence.
Stage 2: Weaponization
In the weaponization stage, attackers create malware or exploit code to target specific vulnerabilities in the organization’s systems.
Prevention Technologies:
- Advanced Threat Protection (ATP): ATP solutions use sandboxing, behavioral analysis, and machine learning to detect and block unknown threats, including malware and exploit code.
- Vulnerability Management: Implementing a vulnerability management program helps organizations identify and remediate vulnerabilities, reducing the attack surface.
Stage 3: Delivery
In the delivery stage, attackers deliver the malware or exploit code to the target organization, often through phishing emails, infected software updates, or exploited vulnerabilities.
Prevention Technologies:
- Email Security Gateways: Email security gateways can detect and block phishing emails, preventing the delivery of malware and exploit code.
- Endpoint Protection: Endpoint protection solutions, such as antivirus software and endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools, can detect and block malware and exploit code on endpoint devices.
Stage 4: Exploitation
In the exploitation stage, attackers use the delivered malware or exploit code to exploit vulnerabilities in the organization’s systems.
Prevention Technologies:
- Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): IPS solutions can detect and block exploit code, preventing attackers from exploiting vulnerabilities.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): EDR tools can detect and respond to exploitation attempts, providing real-time visibility into endpoint activity.
Stage 5: Installation
In the installation stage, attackers install malware or backdoors on compromised systems, allowing them to maintain access and control.
Prevention Technologies:
- Endpoint Protection: Endpoint protection solutions can detect and block malware and backdoors, preventing attackers from installing malicious software.
- Application Whitelisting: Application whitelisting solutions can prevent unauthorized software from running on endpoint devices, reducing the risk of malware installation.
Stage 6: Command and Control (C2)
In the C2 stage, attackers establish communication channels with compromised systems, allowing them to issue commands and exfiltrate data.
Prevention Technologies:
- Network Traffic Analysis (NTA): NTA solutions can detect and block suspicious communication patterns, preventing attackers from establishing C2 channels.
- Domain Name System (DNS) Security: DNS security solutions can detect and block malicious DNS queries, preventing attackers from establishing C2 channels.
Stage 7: Actions on Objectives
In the final stage, attackers exfiltrate sensitive data, disrupt operations, or achieve their objectives.
Prevention Technologies:
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP solutions can detect and block unauthorized data exfiltration, preventing attackers from achieving their objectives.
- Incident Response: Implementing an incident response plan helps organizations respond quickly and effectively to detected threats, reducing the impact of a successful attack.
Conclusion
The cyber kill chain provides a framework for understanding the stages of a cyber-attack, from initial reconnaissance to exfiltration of sensitive data. By implementing prevention technologies at each stage, organizations can reduce the risk of a successful attack and improve their overall security posture. Remember, a comprehensive security strategy involves a combination of people, process, and technology to prevent, detect, and respond to cyber-attacks.
Join us on Telegram for latest cyber security news.



